w3schools.com writes on various of their pages that
The default character encoding in HTML5 is UTF-8.
Even if you read the full page, you will probably get the impression that when you don’t specify encoding in HTML5, it will fallback/default to UTF-8. Which is simply not true. (UTF-8 is used as default in places like form submission but not when loading and setting encoding of a web page.) Just try creating following sample page:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p> Příliš žluťoučký kůň úpěl ďábelské ódy. </p> </body> </html>
It is displayed in Chrome or Firefox like this:
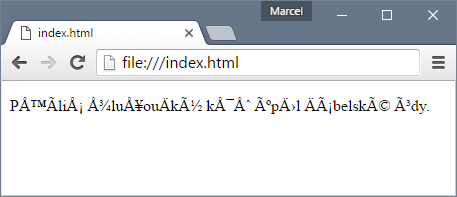
The reason for this is quite obvious. HTML5 specification basically says that it defaults to ASCII-compatible character encoding which can any of many encodings including Windows-1252 (meaning ASCII).
Or as stated in Determining the character encoding, windows-1252 is Suggested default encoding.
So for proper UTF-8 usage there must be UTF-8 BOM at the beginning of the file or you must specify encoding in one of few ways (as w3c requires).